ReEdit: Multimodal Exemplar-Based Image Editing with Diffusion Models
ReEdit: Multimodal Exemplar-Based Image Editing with Diffusion Models
WACV 2025 & ECCV 2024W (AI4VA)
ReEdit is an efficient end-to-end optimization-free framework for exemplar-based image editing. Unlike existing approaches, it doesn't require fine-tuning or optimization during inference time.
Overview
 Figure 1: ReEdit framework architecture showing the three main components: Image Space Edit Capture, Text Space Edit Capture, and Content Preservation for exemplar-based image editing.
Figure 1: ReEdit framework architecture showing the three main components: Image Space Edit Capture, Text Space Edit Capture, and Content Preservation for exemplar-based image editing.
Given a pair of exemplar images (original and edited), ReEdit captures the edit and applies it to a test image to obtain the corresponding edited version. The framework consists of three main components:
- Image Space Edit Capture: Uses pretrained adapter modules to capture edits in the image embedding space
- Text Space Edit Capture: Incorporates multimodal VLMs for detailed reasoning and edit description
- Content Preservation: Conditions image generation on test image features and self-attention maps
Key Features
- No fine-tuning or optimization required during inference
- ~4x faster than baseline methods
- Preserves original image structure while applying edits
- Works with various types of edits
- Model-agnostic (independent of base diffusion model)
Method
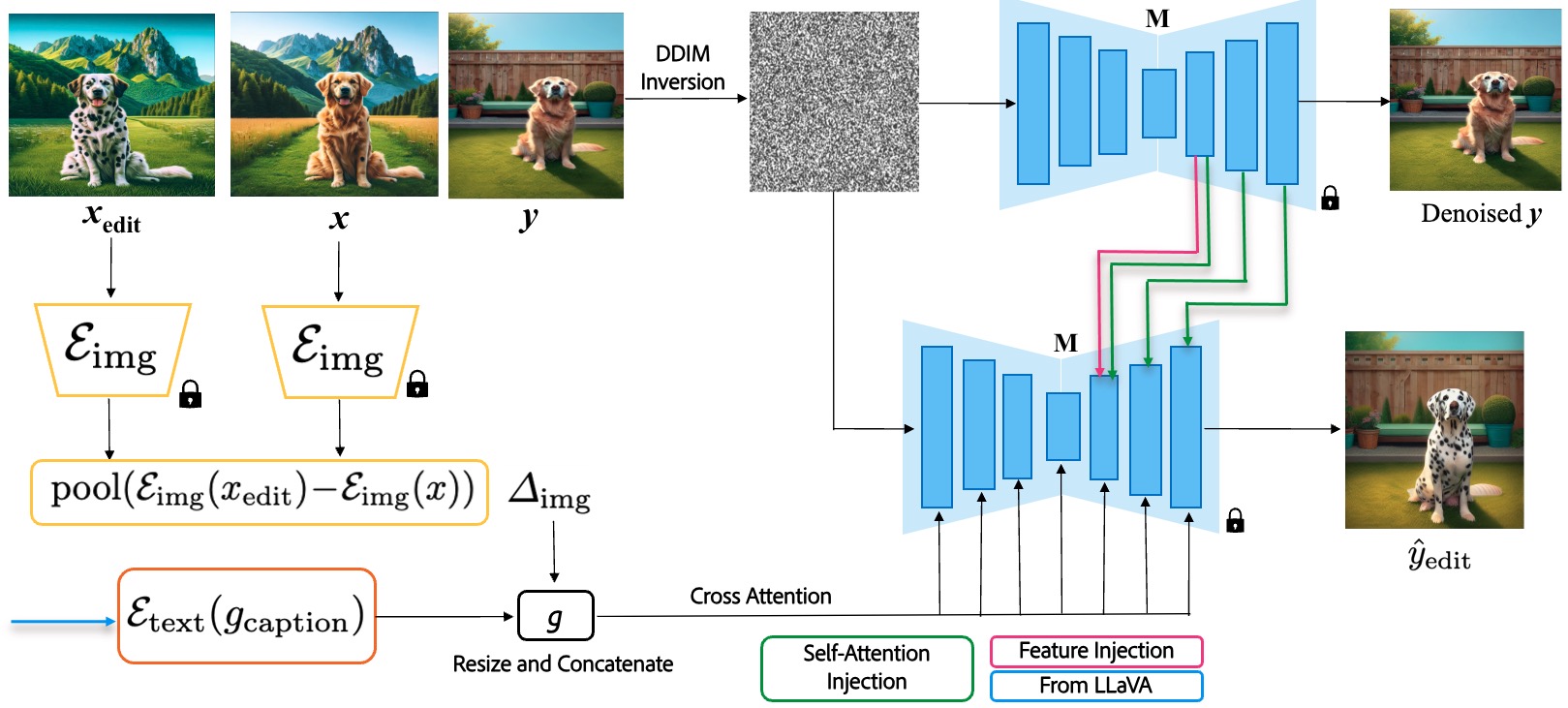 Figure 2: ReEdit framework architecture showing the three main components: Image Space Edit Capture, Text Space Edit Capture, and Content Preservation for exemplar-based image editing.
Figure 2: ReEdit framework architecture showing the three main components: Image Space Edit Capture, Text Space Edit Capture, and Content Preservation for exemplar-based image editing.
Our method involves a sophisticated process of exemplar-based image editing using diffusion models. The approach begins with extracting image embeddings from both the original image $x$ and the edited exemplar $x_{\text{edit}}$ using the encoder $\mathcal{E}{\text{img}}$. The difference between these embeddings is pooled to form $\Delta{\text{img}}$, capturing the nuanced details of the edit. Simultaneously, text guidance is incorporated through $\mathcal{E}{\text{text}}(g{\text{caption}})$, providing additional context for the edit. These components are combined into a guidance vector $g$, which is used to condition the diffusion model $M$.
The process involves DDIM inversion to map the target image $y$ into a latent space, followed by denoising to maintain the structural integrity of the original image. The model employs cross attention, self-attention injection, and feature injection to ensure precise and contextually relevant edits. This method allows for high-quality image transformations that respect the original content while applying the desired changes, as demonstrated in the final output $\hat{y}_{\text{edit}}$.
Dataset Creation
The dataset used for evaluation consists of a diverse range of edits, carefully curated to ensure a comprehensive representation of various editing techniques. The table below summarizes the types of edits included in the dataset:
| Type of Edit | Number of Examples | |---|---| | Global Style Transfer | 428 | | Background Change | 212 | | Localized Style Transfer | 290 | | Object Replacement | 366 | | Motion Edit | 14 | | Object Insertion | 164 | | Total | 1474 |
Summary and statistics of the types of edits in the evaluation dataset. Special care was taken to ensure diversity of edit categories.